- Why Payment Middleware Matters More Than Ever
- The Essential Role of Payment Middleware in eCommerce
- The New Pressures on Payment Middleware Teams
- KPIs Every IT Leader Should Watch in Payment Middleware
- Policies and Practices to Future-Proof Your Payment Middleware
- The Future of Payment Middleware in Italy
- Want to go even deeper into preparing your payment middleware for Italy’s digital surge?
Preparing Your Payment Middleware for the Surge in eCommerce and Digital Payments in Italy
Why Payment Middleware Matters More Than Ever
eCommerce in Italy is growing at a phenomenal pace. The Italian eCommerce market is expected to surpass 61 billion EUR by 2028, building on over €47.1 billion in 2024 (which grew by nearly 10% over 2023). At the same time, digital payments are surging, exceeding €223 billion in the first half of 2024 alone.
These trends are reshaping how businesses operate. Italian consumers demand instant, seamless digital experiences—whether they’re buying clothing, booking holidays, or paying utility bills.
At the center of this transformation is an often-unseen hero: payment middleware. For IT leaders in Italy, preparing this middleware layer for the exponential growth in transactions isn’t optional—it’s essential for business continuity, security, and customer trust.
The Essential Role of Payment Middleware in eCommerce
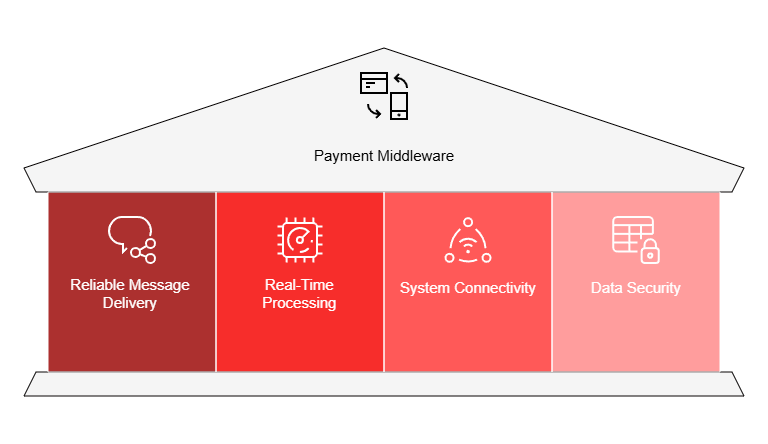
Payment middleware acts as the backbone of digital commerce. It:
- Guarantees reliable message delivery between applications.
- Processes payments in real time.
- Connects diverse systems, databases, and APIs.
- Safeguards sensitive financial data.
Common middleware technologies used by businesses operating in Italy include:
- IBM MQ for robust message queuing.
- Apache Kafka for high-volume streaming.
- ActiveMQ for distributed messaging.
- IBM AppConnect Enterprise (ACE) for complex integrations and transformations.
However, as eCommerce and digital payments grow, these systems face increasing stress. IT leaders must be proactive in managing them—or risk performance failures that directly impact customer satisfaction and revenue.
The New Pressures on Payment Middleware Teams
For IT leaders in Italy, the rapid growth of digital commerce brings specific challenges:
1. Explosive Transaction Volumes
Even a modest uptick in users can translate into millions of additional messages daily. Middleware queues and topics can quickly fill, leading to delays, timeouts, or transaction failures.
IT teams must plan for capacity growth and proactively monitor systems for early warning signs.
2. Demand for Real-Time Transactions
Customers in Italy expect immediate payment confirmations, shipping updates, and account changes. Middleware systems must guarantee real-time data flow and ultra-low latency—even under peak loads.
Failure to deliver instant digital experiences can lead to customer churn and damage brand reputation.
3. Complex Integration Ecosystems
Payment middleware doesn’t operate in isolation. It connects payment processors, banks, loyalty systems, CRM software, fraud prevention services, and numerous APIs.
Each integration adds potential points of failure. IT leaders must maintain visibility into how each component impacts transaction performance.
4. Compliance and Security
Middleware handles highly sensitive data, making it a prime focus for compliance with GDPR, PSD2, and other regulations.
IT leaders must ensure:
- Data is securely transmitted and stored.
- Systems provide auditable records of every transaction and administrative action.
- User access is carefully controlled.
5. Resource Constraints on Middleware Teams
Middleware teams are often small but now must manage large, distributed environments. Manual oversight doesn’t scale. Leaders must look for ways to streamline operations and empower teams to act quickly.
KPIs Every IT Leader Should Watch in Payment Middleware

Monitoring middleware effectively requires tracking the right metrics. While each business may have unique needs, here are some common critical KPIs that IT leaders in Italy should integrate into their operational dashboards. These KPIs are specific enough to be actionable and align with what advanced solutions support today:
For IBM MQ Environments:
- Queue Depths: Indicates potential message backlogs.
- Last Get/Put Times: Measures responsiveness of queues.
- Uncommitted Messages: Helps spot transactions stuck in process.
- Channel Status: Shows whether connections are active, paused, or in error.
For Apache Kafka:
- Under-Replicated Partitions: Alerts you to risks in data consistency.
- Consumer Lag: Measures delay between message production and consumption.
- Broker CPU/Memory Usage: High resource utilization can signal performance issues.
- Leader Election Rate: Frequent leader changes can point to cluster instability.
For ActiveMQ:
- Queue Message Count: High counts may indicate bottlenecks.
- Memory Usage Percentage: Ensures brokers have headroom for message spikes.
- Scheduled Messages: Monitors deferred message loads that could impact throughput.
For IBM ACE:
- Message Flow Execution Times: Helps pinpoint performance bottlenecks.
- Integration Node Status: Confirms that runtime environments remain healthy.
- Active Threads: High counts can signal excessive load.
Cross-Technology KPIs:
- Message Throughput Rates: Are volumes within safe operating ranges?
- Failed Transactions or Retries: A spike may indicate systemic issues.
- SSL Certificate Expiry Dates: Avoid outages due to expired certificates.
- Audit Logs and Event Counts: Track changes and potential unauthorized actions.
Regularly reviewing these KPIs allows IT teams to detect and respond to anomalies quickly—before they escalate into customer-facing problems. Talk to an Avada Software expert to learn how Infrared360’s purpose-built administration and monitoring solution can help you track and automate performance for these KPIs.
Policies and Practices to Future-Proof Your Payment Middleware
Beyond monitoring metrics, IT leaders in Italy should consider policies and operational strategies to ensure their payment middleware is ready for growth:
Implement Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
As digital commerce grows, more users—from developers to operations staff—will need middleware access. RBAC ensures:
- Users see only what they’re permitted to see.
- Sensitive systems remain protected.
- Compliance requirements are met
Policies should define roles for administrators, developers, auditors, and business users.
Establish Synthetic Testing Protocols
Don’t wait for real transactions to test new configurations. Synthetic testing:
- Simulates real payment flows.
- Validates middleware behavior under load.
- Identifies potential bottlenecks before go-live.
Leaders should establish routine synthetic testing for pre-production and production environments.
Automate Incident Responses
Modern middleware environments should be configured to:
- Automatically restart failed channels.
- Clear queues when thresholds are breached.
- Reroute transactions from Dead Letter Queues (DLQs).
These automated “self-healing” capabilities reduce manual workload and downtime.
Schedule Regular Certificate Reviews
Expired SSL or TLS certificates can halt transactions and damage trust. Policies should require:
- Periodic scanning of certificate expiration dates.
- Alerts when certificates near expiry.
- Documented renewal processes.
Centralize Audit Logging
With stricter compliance requirements, IT leaders must maintain comprehensive logs of:
- Administrative changes.
- User access events.
- Transaction-level activity.
Audit trails simplify compliance reporting and help detect suspicious activity.
The Future of Payment Middleware in Italy
The eCommerce and digital payments boom in Italy is exciting—but it raises the bar for IT readiness. Payment middleware will become either a competitive advantage or a critical vulnerability.
IT leaders in Italy must prepare now. That means:
- Tracking detailed KPIs to ensure system health.
- Implementing robust security and compliance measures.
- Empowering teams with unified visibility and automation.
Middleware isn’t just technology—it’s the gateway to customer trust, revenue protection, and competitive success in Italy’s evolving digital economy.
Want to go even deeper into preparing your payment middleware for Italy’s digital surge?
More Infrared360® Resources