- Understanding Middleware: The Backbone of IT Integration
- The Role of Middleware in Modern IT Infrastructure
- The Importance of Middleware Monitoring in IT
- Understanding Middleware Monitoring
- Essential Components and Technologies in Middleware Monitoring
- Why Middleware Monitoring is Critical for Business Success
- Benefits of Middleware Monitoring
- Challenges in Middleware Monitoring
- Popular Middleware Monitoring Tools
- Best Practices for Middleware Monitoring
- Future Trends in Middleware Monitoring
- Conclusion
- Additional Resources

The Ultimate Guide to Middleware Monitoring: Everything You Need to Know
This guide will explain middleware monitoring, why it’s essential, and how it benefits your IT infrastructure. Effective monitoring becomes crucial as businesses rely on diverse middleware technologies to streamline communication between software elements.
We will explore the importance of middleware monitoring, its key benefits, challenges, and the features of robust monitoring solutions. Whether you’re working with IBM® MQ, Apache Kafka, IBM App Connect Enterprise, Oracle WebLogic, or other middleware technologies, this guide provides insights, best practices, and the latest trends to ensure your middleware environment operates seamlessly and efficiently.
Understanding Middleware: The Backbone of IT Integration
Middleware is a critical component in IT infrastructure, acting as a bridge that enables seamless communication and integration between different software applications and systems. Positioned between the operating system and applications, middleware provides a standardized platform for integration, orchestration, and collaboration, ensuring that diverse systems can work together efficiently.
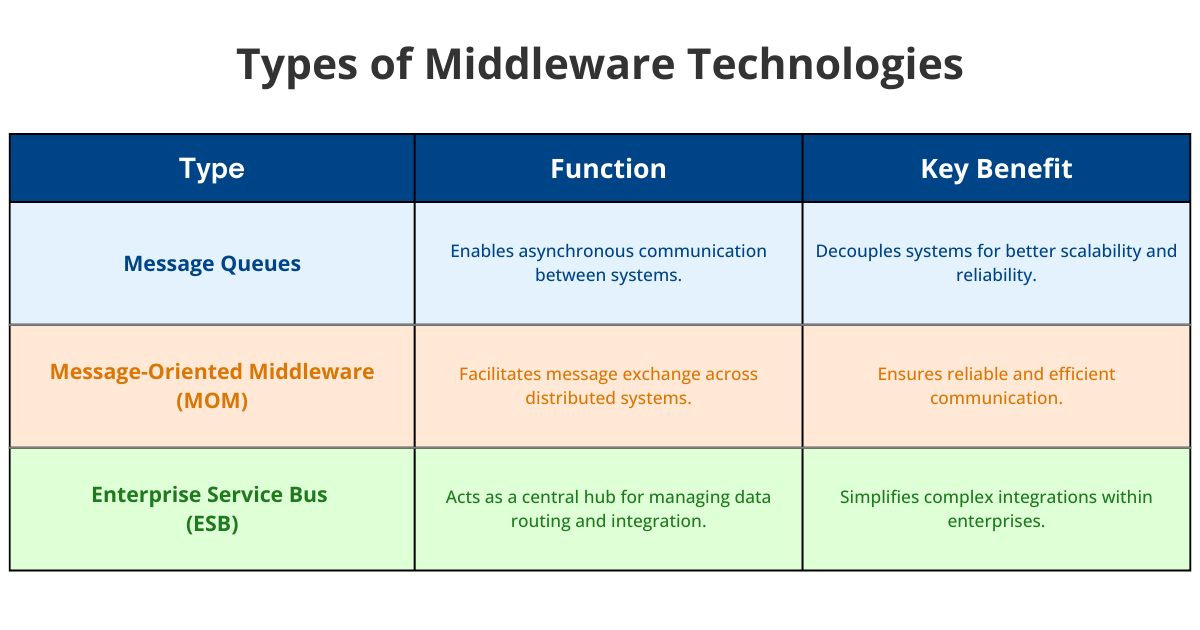
Types of Middleware Technologies
Middleware technologies come in various forms, each designed to address specific integration needs. Here are some common types:
- Message Queues: Facilitate asynchronous communication, allowing systems to exchange data without needing to be active simultaneously. This decouples systems, improving scalability and reliability.
- Message-Oriented Middleware (MOM): Focuses on enabling message exchange between distributed systems, ensuring reliable and efficient communication across networks.
- Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs): Act as a central hub for managing complex routing scenarios, transforming data formats, and integrating multiple applications within an enterprise.
Why Middleware Matters
Middleware is essential for optimizing interactions between software applications and systems. By providing a standardized framework, it ensures system reliability, scalability, and flexibility. Understanding and monitoring middleware is crucial for maintaining smooth IT operations and enabling seamless integration across your technology stack.
Now that we understand the importance of middleware, let’s explore its role in modern IT infrastructure.
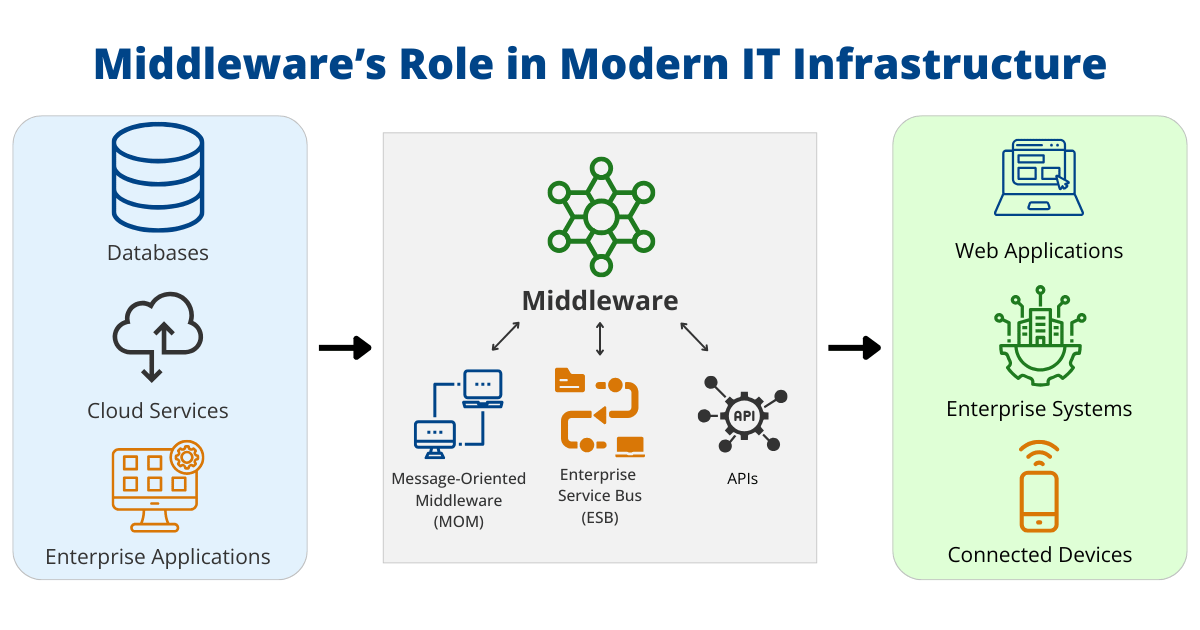
The Role of Middleware in Modern IT Infrastructure
Middleware is a cornerstone of modern IT infrastructure, playing a vital role in connecting and coordinating diverse systems and applications. By enabling efficient communication, integration, and data flow, middleware ensures that organizations can operate in an agile, scalable, and interoperable manner. It acts as the glue that holds complex IT ecosystems together, allowing businesses to adapt to changing technological demands.
Key Middleware Components
Middleware encompasses several key components, each designed to address specific integration challenges. Here are the most important ones:
- Message-Oriented Middleware (MOM): Ensures reliable message exchange between applications, even in distributed environments. This is critical for maintaining communication across systems that may not always be online simultaneously.
- Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs): Facilitate complex service-oriented architectures by managing data routing, transformation, and integration between multiple applications.
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs): Enable seamless communication between software components, allowing developers to build interconnected systems with ease.
Middleware as a Bridge Between Legacy and Modern Systems
One of middleware’s most significant advantages is its ability to bridge the gap between legacy systems and modern applications. This allows organizations to maximize their existing IT investments while adopting new technologies. By acting as a strategic enabler for digital transformation, middleware ensures that businesses can pursue efficiency, connectivity, and agility without being hindered by the complexities of their IT ecosystems.
To ensure middleware continues to perform effectively, monitoring is essential.
The right monitoring approach can make all the difference. See how Infrared360 simplifies middleware monitoring with real-time insights and agentless visibility.
The Importance of Middleware Monitoring in IT
Middleware monitoring is essential for optimizing system performance in enterprise environments. It provides real-time insights into the health and efficiency of middleware systems, which act as the glue connecting applications, databases, and services. By tracking metrics like message queues, transaction rates, and resource utilization, organizations can ensure their middleware operates at peak performance and responsiveness.
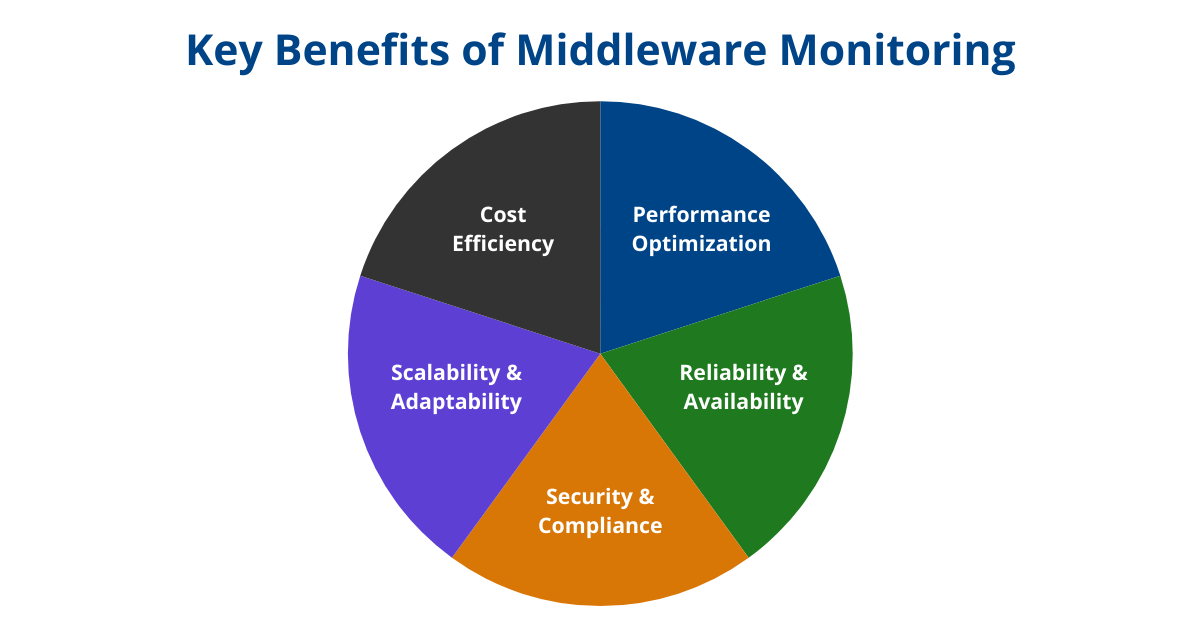
Middleware monitoring addresses several critical areas to maintain a robust IT infrastructure:
- Performance Optimization:
Ensures optimal response times and efficient resource allocation, improving system performance and user experience. Proactive monitoring helps detect issues early, enabling timely interventions and reducing downtime. - Reliability and Availability:
Maintains the reliability and availability of critical business applications by identifying and resolving bottlenecks or performance degradation, ensuring uninterrupted operations. - Security and Compliance:
Safeguards sensitive information by detecting unauthorized access, potential breaches, and anomalies in data transmissions. It also helps organizations meet regulatory requirements. - Scalability and Adaptability:
Provides insights into system scalability, helping businesses plan for growth and optimize middleware architectures to remain adaptable. - Cost Efficiency:
Reduces unexpected downtime, lowers mean time to repair (MTTR), and optimizes resource utilization, leading to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Understanding Middleware Monitoring
Middleware serves as the backbone of modern IT infrastructures, facilitating communication between disparate systems. It relies on technologies such as:
- Message-Oriented Middleware (MOM): Ensures reliable message delivery.
- Enterprise Service Buses (ESBs): Manages complex routing and service-oriented architectures.
- Integration Platforms: Supports diverse integration needs.
Middleware monitoring tracks key metrics and activities, including:
- Message Queues: Monitors the flow and status of messages.
- Transaction Rates: Measures the frequency and success of transactions.
- Resource Utilization: Tracks the use of computational resources like CPU and memory.
- System Responsiveness: Ensures timely interactions between systems.
The primary goal is to identify and resolve potential issues, bottlenecks, or anomalies before they disrupt business operations.
Why Middleware Monitoring Matters
Effective middleware monitoring provides real-time insights into the performance of interconnected systems. It enables IT teams to:
- Detect anomalies and address issues proactively.
- Track critical metrics like message queues, transaction rates, and resource utilization.
- Ensure optimal performance and responsiveness of middleware systems.
Key Benefits of Middleware Monitoring
- Enhanced System Reliability:
Minimizes downtime by identifying and resolving bottlenecks or performance degradation, ensuring uninterrupted business operations. - Improved Performance Optimization:
Offers a comprehensive view of middleware health, helping maintain optimal system responsiveness. - Strengthened Security:
Detects suspicious activities or potential security breaches, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. - Streamlined Compliance and Governance:
Generates detailed reports on system performance and transactional activities, supporting adherence to IT governance policies.
Actionable Insights for Effective Middleware Monitoring
To maximize the benefits of middleware monitoring, organizations must be prepared to act on the data and alerts it provides. Key steps include:
- Invest in the Right Tools:
Choose monitoring solutions that offer secure, permission-based administrative and testing capabilities, ensuring they align with your organization’s specific needs. - Build Expertise:
Train IT teams to respond effectively to incidents and develop a proactive approach to system management. - Adopt a Proactive Mindset:
Use monitoring data to anticipate and address potential issues before they escalate, continuously optimizing system performance based on insights.
To fully leverage middleware monitoring, it’s crucial to understand its essential components and the technologies that power it. In the next section, we’ll explore the key elements of middleware monitoring systems and the tools that enable organizations to maintain seamless, secure, and high-performing IT environments
Essential Components and Technologies in Middleware Monitoring
Effective middleware monitoring relies on several key components and technologies that provide comprehensive insights into system performance and health. Understanding these elements is essential for optimizing middleware environments and ensuring seamless digital operations.
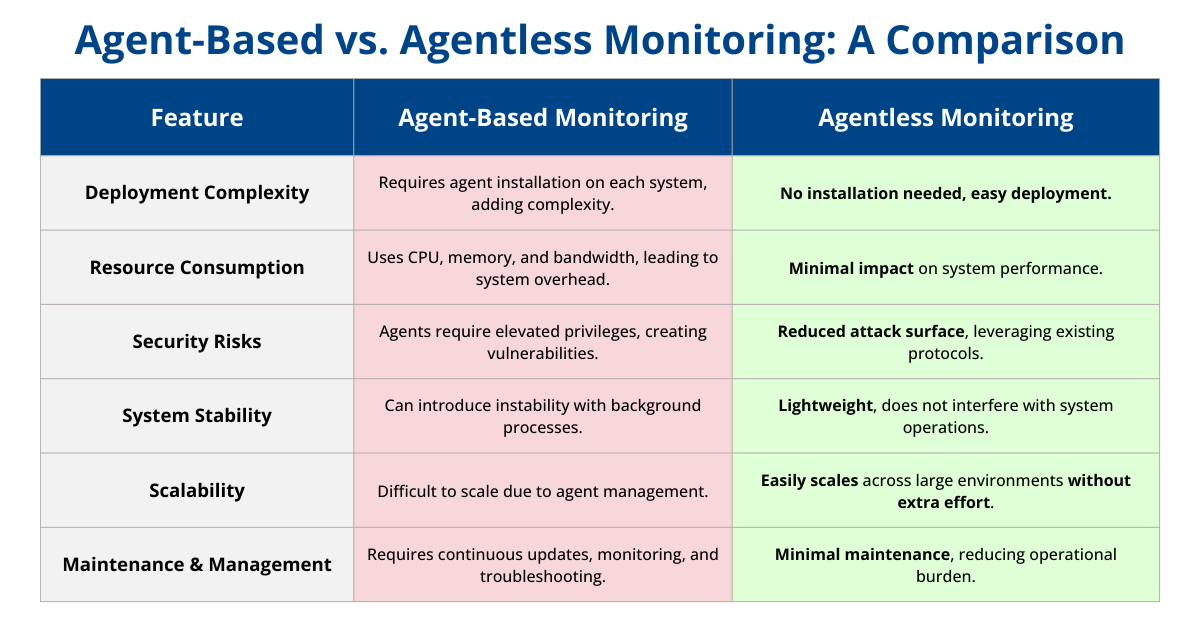
Monitoring Agents
Many middleware monitoring solutions require the deployment of agents, which play a crucial role in gathering data for system analysis and performance evaluation. However, they come with inherent challenges and drawbacks that organizations must consider.
Challenges of Monitoring Agents
- Resource Consumption: Monitoring agents consume CPU, memory, and network bandwidth, contributing to “agent overhead.” This can be particularly problematic in large-scale deployments and potentially affect system performance.
- Complex Management: Managing and maintaining multiple agents across diverse environments can be complex and resource-intensive.
- System Stability: Continuous background activity from agents can introduce unpredictability, impacting overall system stability.
- Security Risks: Agents often have elevated privileges, making them potential cyberattack targets. If compromised, they could allow unauthorized access to sensitive data or control monitored systems.
- Vulnerabilities: Agent software vulnerabilities or misconfigurations can expose security weaknesses, requiring vigilant updates and configurations.
Agentless Solutions
Agentless middleware monitoring solutions offer several benefits, making them an attractive choice for efficient and streamlined monitoring processes:
- Simplified Deployment: Eliminates the need to install and manage agents on individual servers or systems, simplifying the deployment process.
- Reduced Security Risks: Minimizes potential security risks associated with agent-based solutions by relying on existing protocols and interfaces.
- Lower Resource Consumption: Gathers essential data without the overhead of agent installations, preventing performance impact on monitored systems.
- Enhanced Scalability: The centralized and lightweight nature of agentless monitoring enhances scalability, flexibility, and ease of maintenance.
- Resource Efficiency: Optimal for organizations prioritizing simplicity and resource efficiency in their monitoring strategies.
Alerting & Notifications
Alerting mechanisms are crucial for identifying and addressing real-time issues, but they must be managed carefully to prevent alert fatigue.
Avoiding Alert Fatigue
Alert fatigue in IT operations occurs when excessive or irrelevant alerts overwhelm workers, leading to desensitization, reduced responsiveness, and poor decision-making. Practical strategies to combat alert fatigue include:
- Fine-Tuning Alert Configurations: Ensure alerts are relevant and precise to reduce unnecessary notifications.
- Providing Contextual Alerts: Offer context to help prioritize and address critical issues promptly.
- Prioritizing and Categorizing Alerts: Focus on critical alerts to address essential issues effectively.
Ensuring that your middleware monitoring solution allows for role-based alert notifications—targeting only the specific individuals who need to know and have permission to act—is critical for avoiding alert fatigue and maintaining system stability and security.
Dynamic Alert Parameters
Fine-tuning alert configurations is crucial for minimizing maintenance efforts and reducing data retention costs. Advanced monitoring solutions simplify this process by offering:
- Granular, Role-Based Alert Configuration: Empower administrators to align alerts with specific team responsibilities and expertise.
- Complex, Nested Rule Sets: Utilize parameter stacking (e.g., “and this” and “or that”) to establish practical and useful alert criteria.
Alert Channels
Modern middleware monitoring is effective only if alert notifications are prominently displayed on-screen and tied to the object being monitored. Notifications should also be sent through multiple channels, such as email and text. Integration with third-party systems, such as ticketing systems, is crucial for ensuring timely responses.
Secure Permissions-Based Visibility
Secure permissions-based visibility ensures that sensitive data and operations are protected from unauthorized access while allowing sufficient transparency for monitoring and management tasks. This approach leverages role-based access control (RBAC) to define who can view or interact with the middleware environment.
Implementing Secure Permissions
- Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Establish specific roles aligned with the organization’s security policies.
- Enforce Through Tools: Use middleware monitoring tools to enforce these roles and responsibilities.
- Dynamic Access Controls: Adjust permissions as roles or business needs change, ensuring ongoing alignment with security policies.
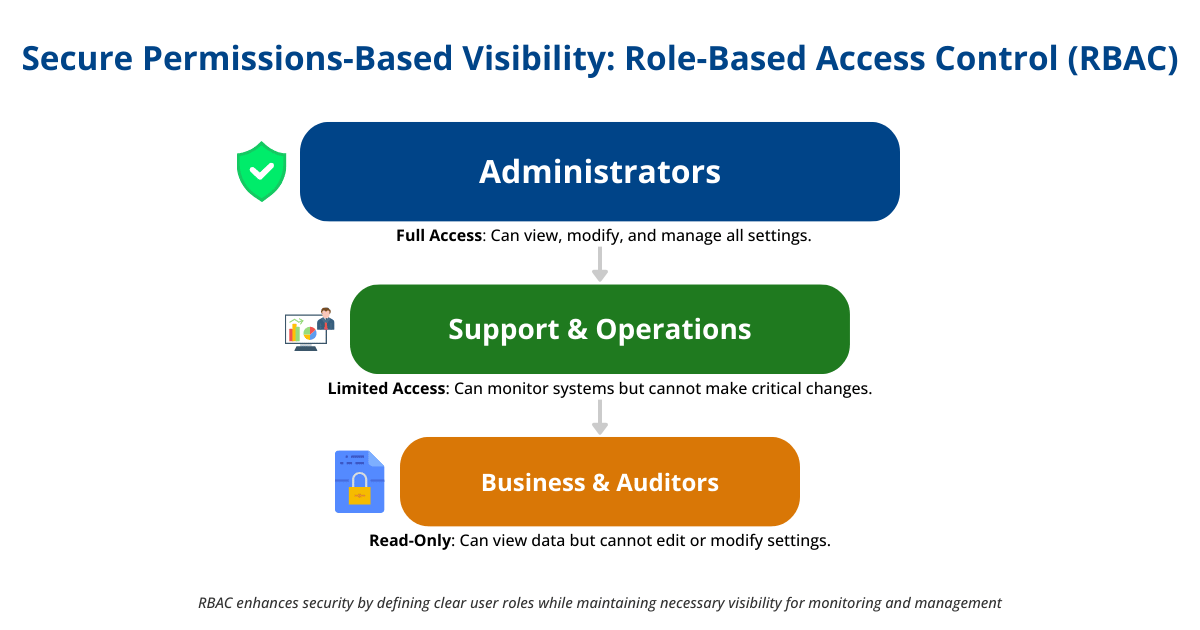
This approach enhances security by restricting access to sensitive information and allows for effective monitoring and management of the middleware environment.
Real-Time Middleware Monitoring
Real-time monitoring refers to tracking and responding to events as they occur within the middleware infrastructure. This capability is crucial for identifying and mitigating issues before they impact business operations.
Importance of Real-Time Monitoring
- Immediate Issue Identification: Track events as they happen to identify and address potential problems quickly.
- Meeting SLAs: Many organizations have Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that require timely issue resolution. Real-time data is critical to meeting these SLAs.
- Preventing Delays: Ensure monitoring solutions provide real-time alerts based on actual data rather than logs to avoid delays in issue identification and response.
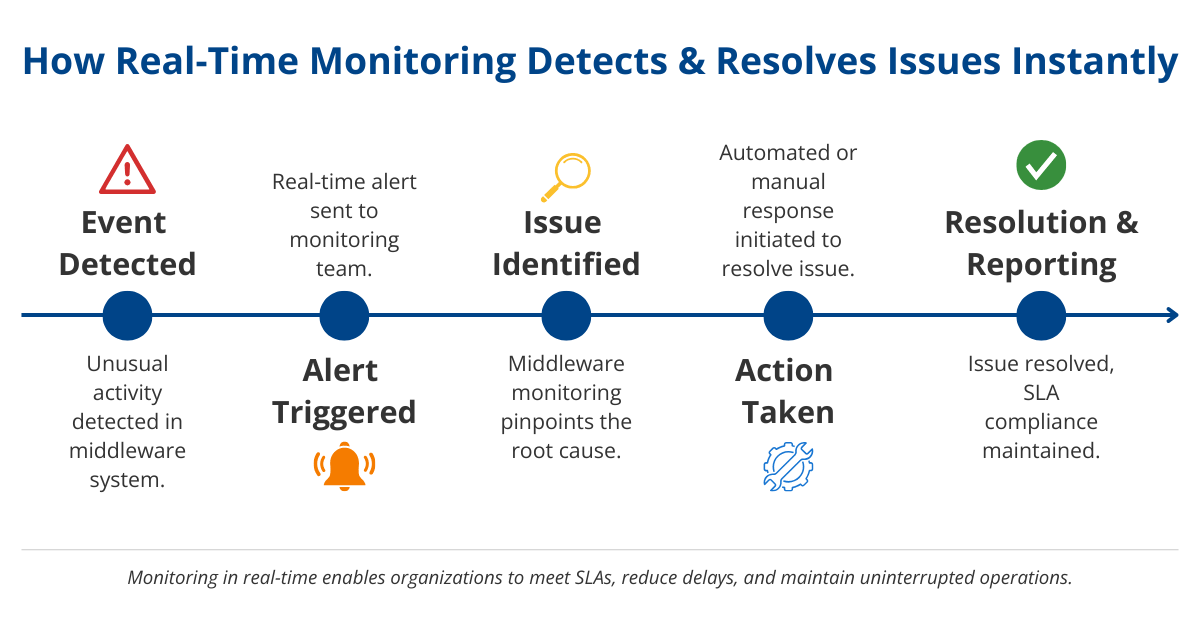
Best Practices for Real-Time Monitoring
- Accurate Alerts: Ensure monitoring solutions alert off real-time data rather than writing data to logs and then alerting off averages in those logs, which can delay response times.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Monitor all critical components of the middleware infrastructure to ensure comprehensive visibility and quick issue resolution.
Single Pane of Glass

The legacy definition of a “single pane of glass” referred to monitoring multiple middleware types under a unified tool. The modern concept expands this to include a unified management interface that consolidates all middleware monitoring information and enables secure, permission-based administrative actions in one accessible location.
Designing an Effective Single Pane of Glass
- Data Integration: Integrate various data sources to ensure comprehensive visibility.
- User-Friendly Interface: Ensure the interface is user-friendly and customizable to meet the needs of different users.
- Scalability: Support scalability to handle increasing numbers of users, data, and functionality.
A practical single pane of glass allows IT teams to manage middleware environments more efficiently, streamline operations, and make informed decisions quickly.
Audit Trails
Native administrative capabilities within middleware monitoring tools allow for direct interaction and management of middleware components. These features ensure administrators can efficiently perform maintenance tasks, updates, and troubleshooting without relying on third-party tools.
Maintaining Effective Audit Trails
- Automated Logging: Implement automated logging of all significant actions to ensure comprehensive tracking.
- Tamper-Proof Logs: Ensure that logs are tamper-proof to maintain integrity.
- Retention Period: Retain logs for a period dictated by regulatory and business needs.
Analysis Tools
- Pattern Identification: Use analysis tools to make sense of the data and identify patterns or anomalies.
- Native Analysis Capabilities: Middleware monitoring solutions should have built-in analysis tools to facilitate quick and accurate assessments.
Native Administrative Capabilities
Native administrative capabilities within middleware monitoring tools allow for direct interaction and management of middleware components. These features ensure administrators can efficiently perform maintenance tasks, updates, and troubleshooting without relying on third-party tools.
Benefits of Native Administrative Capabilities
- Efficient Maintenance: Enable administrators to perform tasks directly within the monitoring tool, streamlining the process.
- Permission-Based Access: Provide secure, permission-based access for delegated administration, promoting a collaborative approach to issue resolution.
- IT Self-Help/Self-Service: Foster a secure environment where IT staff can resolve issues independently, improving response times and reducing reliance on central administration.
Integration
Middleware monitoring tools should seamlessly integrate with existing IT management frameworks and protocols to avoid creating silos and enhance collaboration.
Key Integration Points
- Ticketing Systems: Integration with ticketing systems ensures efficient tracking and resolution of issues.
- Graphic Analytics Tools: Connect with graphic analytics tools to provide visual data representations for better analysis and decision-making.
- Central Monitoring Consoles: Integrate with central monitoring consoles to consolidate data and provide a unified view of system health and performance.
Technologies
Middleware monitoring relies on various technologies to ensure optimal performance, security, and compliance.
Data Processing and Analytics
- Stream Processing Engines: Tools like Apache Kafka and Apache Storm for real-time data processing.
- Real-Time Analytics Platforms: Platforms that provide insights into data as it is processed.
Security and Access Management
- Advanced Encryption Standards: Ensures data security during transmission and storage.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM) Solutions: Manages user identities and access permissions.
User Interface and Experience
- Web-Based Interfaces: Accessible and user-friendly interfaces for ease of use.
- Customizable Dashboards and Widgets: Allows users to tailor their view and access relevant information quickly.
Logging and Compliance
- Centralized Log Management Solutions: Tools like ELK Stack and Splunk for comprehensive log management.
- Compliance Management Software: Ensures adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies.
Integration and Automation
- API Management Platforms: Facilitates integration and management of APIs.
- Automation and Orchestration Tools: Tools such as Ansible and Terraform are utilized to automate and orchestrate tasks.
Now that we’ve explored the essential components and technologies in middleware monitoring, let’s examine why effective monitoring is critical for driving business success and maintaining competitive advantage.
Why Middleware Monitoring is Critical for Business Success
Middleware monitoring is essential for business success as it serves as the technological glue that connects different applications, systems, and services within an organization. By effectively monitoring middleware, businesses can ensure smooth and efficient communication between disparate software components, which is crucial in a world where digital operations and services are increasingly interconnected.
Secure Collaboration Across Teams
Modern IT departments need to securely collaborate across different teams to manage middleware effectively. Middleware interacts with various parts of an organization’s IT infrastructure, from databases and user interfaces to external services. Identifying and resolving issues often require coordinated efforts among multiple teams, including development, operations, and security. Effective middleware monitoring solutions provide these teams with a unified view of system performance and anomalies, facilitating:
- Accelerated Problem Resolution: Unified monitoring tools allow for quicker identification and resolution of issues, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Security: Ensuring that all actions taken on the system are logged and auditable improves security and compliance.
- Streamlined Communication: A unified view helps teams collaborate more effectively, sharing insights and strategies for optimizing system performance.
Real-Time Alerts and Immediate Response
The ability to act on real-time alerts is another cornerstone of modern middleware monitoring. In today’s fast-paced digital environment, delays in detecting and responding to issues can lead to significant disruptions and financial losses. Real-time monitoring and alerts enable businesses to:
- Identify Issues Immediately: Quickly pinpoint potential problems before they impact users or escalate into more significant issues.
- Minimize Downtime: Rapid response to alerts helps maintain system uptime and reliability.
- Maintain Quality of Service: Consistent monitoring ensures that service levels remain high, which is vital for customer satisfaction and trust.
Adapting to Complex and Dynamic Environments
With the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and microservices architectures, middleware has become more complex and dynamic. Traditional periodic checks are no longer sufficient. Modern monitoring tools continuously analyze data across the network, providing insights that help:
- Anticipate Potential Failures: Proactive analysis helps identify vulnerabilities and prevent issues before they occur.
- Optimize System Performance: Continuous monitoring enables ongoing performance improvements, ensuring that systems run efficiently.
- Adapt to Changes: Real-time data analysis helps businesses adjust to changes in their IT environment, maintaining stability and performance.
Middleware monitoring is thus critical for ensuring business success by enabling secure collaboration, immediate response to issues, and proactive performance management in complex IT environments.
Effective middleware monitoring enables seamless collaboration, rapid response, and proactive optimization. Discover how Infrared360 provides real-time insights and secure, role-based visibility to keep your IT environment running smoothly
Benefits of Middleware Monitoring
Middleware monitoring offers a range of benefits crucial for maintaining a robust and efficient IT infrastructure within an enterprise. Highlighting these benefits showcases how monitoring can significantly impact business success.
Real-Time Visibility
Middleware monitoring provides real-time visibility into the performance and health of various middleware components. This visibility allows IT teams to promptly identify issues, bottlenecks, or anomalies, enabling quick responses to ensure optimal system operation.
- Immediate Insights: Access to real-time data helps IT teams stay informed about system status and potential issues.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Real-time visibility supports informed decision-making for system improvements and troubleshooting.
Proactive Issue Detection
Organizations can detect potential issues by continuously monitoring middleware components before they escalate into critical problems. Proactive monitoring allows IT teams to address issues early, minimizing downtime and reducing the impact on business operations.
- Early Intervention: Detecting issues early helps prevent more significant problems and system failures.
- Reduced Downtime: Proactive issue detection minimizes downtime, maintaining business continuity.
Performance Optimization
Middleware monitoring tools help optimize the performance of interconnected systems by tracking key metrics such as response times, throughput, and resource utilization. This optimization ensures that applications run efficiently, providing a positive user experience and supporting overall business productivity.
- Improved Efficiency: Monitoring tools help fine-tune system performance for better efficiency.
- Enhanced User Experience: Ensures applications perform well, increasing user satisfaction.
Security and Compliance
Monitoring middleware is vital for ensuring the security of data transmissions and compliance with industry regulations. By detecting security breaches, unauthorized access, or anomalies in data flows, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and meet regulatory requirements, safeguarding sensitive information.
- Data Protection: Continuous monitoring helps detect and respond to security threats.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that the organization meets industry regulations and standards.
Scalability Planning
Middleware monitoring aids in planning for scalability by providing insights into existing systems’ capacity and resource utilization. Organizations can identify potential scalability challenges and prepare for infrastructure expansion or optimization to accommodate growing business needs.
- Future-Proofing: Helps plan for future growth and scalability needs.
- Resource Management: Ensures resources are used effectively to support expansion.
Resource Utilization Efficiency
Monitoring middleware helps organizations optimize the utilization of resources such as servers, databases, and messaging queues. Efficient resource management leads to cost savings, improved performance, and a more sustainable IT infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: Efficient resource use reduces operational costs.
- Sustainable IT: Promotes a sustainable approach to IT resource management.
Root Cause Analysis
When issues arise, middleware monitoring tools assist IT teams in performing root cause analysis. By tracing the origin of problems, organizations can implement targeted solutions, reducing the time spent on issue resolution and minimizing the impact on business operations.
- Quick Resolution: Identifies the root cause of issues quickly for faster resolution.
- Targeted Solutions: Enables specific and practical problem-solving strategies.
Cost Reduction
Middleware monitoring is a cost-effective solution. It achieves this by proactively detecting issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring efficient resource utilization. This approach prevents downtime, streamlines operations, and optimizes resource allocation, all of which contribute to a more cost-effective IT environment.
- Operational Savings: Reduces costs associated with downtime and inefficient resource use.
- Streamlined Operations: Enhances overall operational efficiency, contributing to cost savings.
Middleware monitoring is essential for ensuring business success by providing real-time visibility, proactive issue detection, performance optimization, security, and cost efficiency. These benefits collectively enhance the robustness and efficiency of an organization’s IT infrastructure, supporting its strategic goals and operational excellence.
Challenges in Middleware Monitoring
Middleware monitoring is a critical component of modern IT infrastructure, but it comes with its own set of challenges. As organizations adopt diverse middleware technologies to power their operations, they face complexities in managing these environments, scaling their systems, and balancing monitoring overheads with performance. Optimizing monitoring strategies is essential to ensure valuable insights without compromising system efficiency.
Complexities in Diverse Middleware Environments
One of the primary challenges in middleware monitoring is the diverse and complex nature of middleware environments. Many enterprises operate with a mix of messaging systems, application servers, and integration platforms. Each middleware component may have unique monitoring requirements, making it difficult to implement a unified monitoring solution. Differences in protocols, message formats, and communication patterns further add to the complexity.
Overcoming the Complexity
To address these challenges, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
- Flexible Solutions: Use middleware monitoring tools capable of handling various technologies and protocols.
- Unified Interface: Implement a single interface that combines monitoring and administrative capabilities, providing a centralized view of the entire middleware environment.
Scalability Issues with Growing IT Infrastructure
As enterprises grow, their IT infrastructures expand to accommodate increased data volumes, user demands, and business applications. Many middleware monitoring solutions struggle to scale efficiently with this growth, leading to challenges in managing the increased number of endpoints, transactions, and data flows.
Addressing Scalability
To ensure scalability, organizations should consider:
- Scalable Architectures: Implement middleware monitoring architectures that can adapt to growing complexity.
- Agentless Solutions: Use agentless monitoring tools to reduce resource consumption and simplify deployment.
- Horizontal Scalability: Design monitoring strategies that can accommodate the addition of new middleware types and systems without significant reconfiguration.
Balancing Monitoring Overheads with Performance
Middleware monitoring inherently introduces overhead on the systems being monitored, especially when agents are involved. The challenge lies in finding the right balance between obtaining comprehensive monitoring data and minimizing the impact on system performance.
Achieving the Balance
To achieve this balance, organizations can:
- Adopt Agentless Monitoring: Agentless solutions reduce system resource utilization and are ideal for large-scale deployments.
- Use Lightweight Agents: If agents are necessary, opt for lightweight versions that consume fewer resources.
- Implement Intelligent Sampling: Use sampling techniques to collect essential data without overwhelming the system.
- Fine-Tune Configurations: Optimize monitoring settings to ensure efficiency and minimize performance impact.
Other Challenges in Middleware Monitoring
Beyond complexity, scalability, and performance, middleware monitoring faces several additional challenges that organizations must address:
- Volume of Data: High volumes of data generated by middleware components can overwhelm traditional monitoring tools, making storage, processing, and analysis difficult.
- Real-Time Performance: Providing real-time monitoring and alerts without causing performance lags is a significant challenge.
- Complexity of Integration: Middleware often integrates with multiple systems, making monitoring complex due to varied technologies and protocols.
- Dynamic Environments: Monitoring solutions must adapt quickly to changes in the IT environment, such as upgrades or new deployments.
- Security Concerns: Safeguarding monitoring data and ensuring monitoring processes do not introduce new vulnerabilities is critical.
- Alert Fatigue: Managing alerts to ensure critical notifications are not lost in a flood of less-important alerts is a common issue.
- Cost of Monitoring Solutions: The cost of comprehensive monitoring tools must be balanced against the need for detailed and effective monitoring.
- Skill Requirements: Configuring, managing, and interpreting data from monitoring tools requires specialized knowledge, adding to training and staffing challenges.
Cost Efficiency with Middleware-Specific Monitoring Solutions
General IT infrastructure monitoring solutions can extend to middleware environments, but they often come with higher costs due to licensing structures and data storage requirements. Middleware-specific monitoring solutions offer a cost-effective alternative by focusing on efficient data management and storage techniques, providing significant cost savings.
Advantages of Middleware-Specific Solutions
- Cost Savings: Efficient data management and no additional charges for data storage result in year-over-year savings.
- Performance: Minimizes impact on system performance while providing comprehensive monitoring.
- Efficiency: Focuses on middleware-specific needs, ensuring detailed and relevant monitoring without the overhead of generalist tools.
Effective middleware monitoring requires balancing depth of insight with operational overhead. Implementing middleware-specific solutions can provide the necessary visibility into system performance and issues without compromising the overall performance of the IT infrastructure. This strategic choice helps organizations manage costs while monitoring critical systems effectively and efficiently.
Now that we’ve explored the challenges in middleware monitoring, let’s dive into the popular tools available to address these challenges and streamline middleware management.
Popular Middleware Monitoring Tools
Middleware monitoring is essential for maintaining seamless communication between applications and ensuring the performance and reliability of your IT environment. Several tools are commonly used for middleware monitoring, each offering distinct features to meet diverse operational needs. While general-purpose tools can be adapted for middleware environments, purpose-built solutions like Infrared360 provide specialized capabilities tailored to the unique challenges of middleware monitoring.
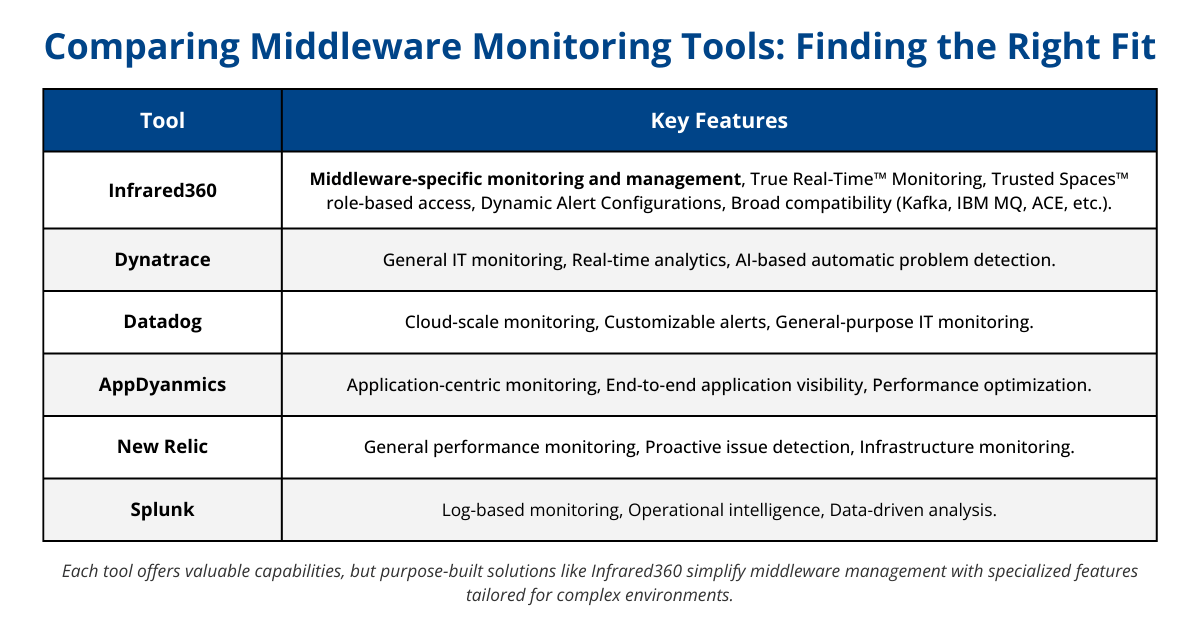
Infrared360: Middleware-Specific Monitoring and Management
Infrared360 is a dedicated middleware monitoring solution that also serves as a complete middleware management portal. Unlike general-purpose tools, Infrared360 focuses exclusively on middleware environments, offering features tailored to the unique requirements of middleware operations:
- True Real-Time™ Monitoring: Provides instant visibility into middleware performance, enabling proactive issue resolution.
- Trusted Spaces™: Enables secure, role-specific access for self-service and delegated administration.
- Dynamic Alert Configurations: Allows IT teams to create highly granular, customized alert setups.
- Role-Based Access Control: Ensures management is aligned with specific team roles and responsibilities.
- Broad Compatibility: Supports cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments, including Kafka, IBM MQ, ActiveMQ, App Connect Enterprise, Application Servers, DataPower, URLs, and Web Services.
With these capabilities, Infrared360 is designed to simplify middleware management while providing comprehensive visibility, control, and scalability.
Dynatrace
Dynatrace is a versatile tool often used for monitoring across applications, databases, and infrastructure. Key features include:
- Real-Time Analytics: Delivers actionable insights for performance optimization.
- Automatic Problem Detection: Uses AI to identify and report issues without manual intervention.
While Dynatrace is well-regarded for general IT monitoring, its capabilities are not specifically tailored for middleware environments. This may necessitate additional configurations or tools for comprehensive middleware management.
Datadog
Datadog is known for its cloud-scale monitoring capabilities and real-time dashboards. It offers:
- Cloud-Scale Monitoring: Supports a wide range of platforms and technologies.
- Alerting: Includes customizable alerts for various systems.
Datadog’s strength lies in its extensive integration options, but its reliance on agents and focus on high-level infrastructure monitoring may require supplementary tools to address middleware-specific challenges.
AppDynamics
Part of Cisco’s suite, AppDynamics specializes in application performance management. Key features include:
- End-to-End Visibility: Monitors business-critical applications and their dependencies.
- Performance Management: Assists in optimizing application performance.
AppDynamics is particularly effective for application-centric monitoring, though it may not provide the middleware-specific visibility needed for in-depth management of middleware environments.
New Relic
New Relic focuses on performance monitoring for applications and infrastructure. Its features include:
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks application and system health.
- Proactive Management: Detects and resolves potential issues before they escalate.
While New Relic excels at performance monitoring, its general-purpose design means middleware-specific configurations may require additional effort or integration with other tools.
Splunk
Splunk is widely recognized for its log management and analysis capabilities. Key features include:
- Operational Intelligence: Uses machine data for insights into IT and business outcomes.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Enables data-driven decision-making through powerful analytics.
Although Splunk is effective for log-based monitoring, its emphasis on machine data may not fully align with the real-time operational needs of middleware environments.
Choosing the Right Tool for Middleware Monitoring
Each of these tools provides valuable capabilities for IT professionals managing complex systems. While general-purpose solutions like Dynatrace, Datadog, AppDynamics, New Relic, and Splunk can be adapted for middleware environments, tools like Infrared360, designed explicitly for middleware, offer purpose-built features and efficiency that can simplify operations and improve response times.
Now that we’ve explored the popular tools for middleware monitoring, let’s dive into the best practices for implementing and optimizing these solutions to maximize their impact.
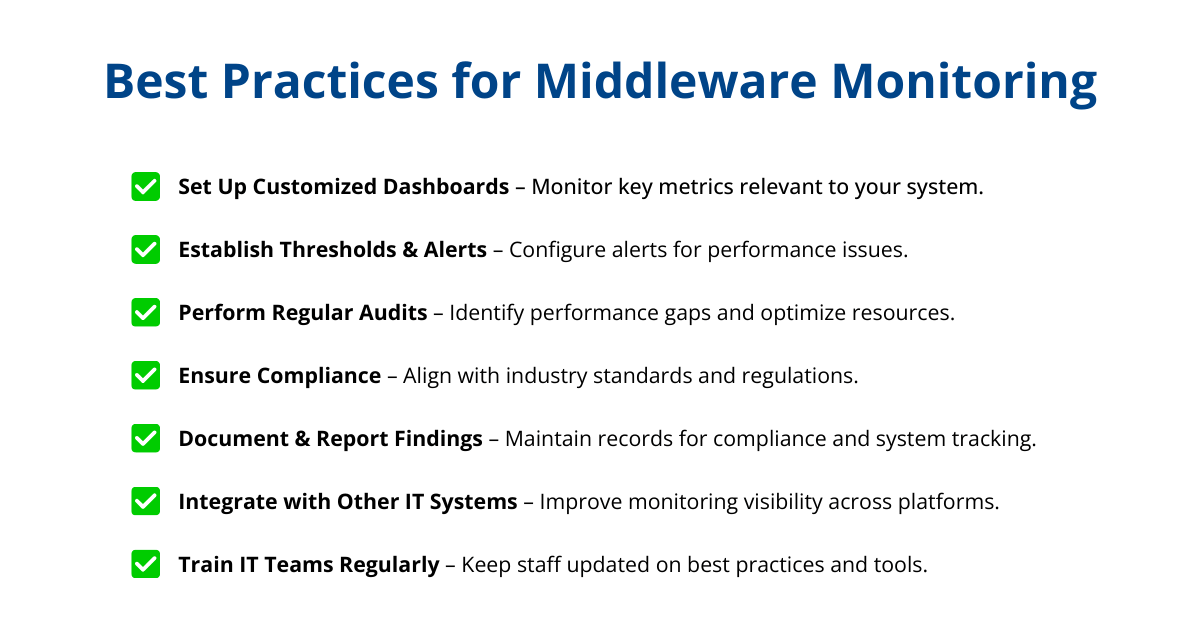
Best Practices for Middleware Monitoring
Implementing best practices for middleware monitoring ensures that your monitoring strategy is effective, efficient, and aligned with your organization’s needs. By following these guidelines, organizations can optimize their middleware environments, enhance system performance, and maintain security and compliance.
Setting Up Customized Monitoring Dashboards
Monitoring dashboards serve as a central platform for observing and analyzing the performance of middleware components. These dashboards provide a visual overview of operational metrics, helping IT professionals quickly assess the health and efficiency of their middleware infrastructure. Customized dashboards are essential because they allow teams to focus on the metrics that matter most to their specific environments and business objectives.
Customization Techniques
- Identify Key Metrics: Start by identifying the most critical metrics that reflect the performance and health of your middleware. Typical metrics include response time, throughput, error rates, and resource utilization.
- User-Centric Design: Design dashboards that are intuitive and easy to use for various user groups. For instance, technical support teams may need detailed operational data, while executive teams prefer high-level performance summaries.
- Modular Layouts: Implement modular dashboard layouts that can be easily modified or expanded as business needs evolve. This flexibility allows for the addition of new metrics or integration with other systems without a complete redesign.
Tools and Technologies
Several tools and technologies can facilitate the creation of effective monitoring dashboards:
- Infrared360: Enables users to analyze data through intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces, making complex data analysis accessible without programming expertise. Users can create and share visual data representations such as dashboards, graphs, charts, and reports.
- Grafana: Popular for its ability to create dynamic and visually appealing dashboards. Grafana supports multiple data sources, including Prometheus and Elasticsearch.
- Splunk: Known for its powerful data processing capabilities, Splunk can be used to create custom dashboards that analyze large volumes of logging data.
Establishing Thresholds and Alerting Mechanisms
Setting appropriate thresholds for performance metrics is crucial in middleware monitoring. These thresholds act as benchmarks for normal operations, and crossing them triggers alerts. Key metrics include CPU usage, memory consumption, and transaction response times. IT personnel should set realistic, effective thresholds reflecting peak and normal operational conditions and regularly review them to adapt to changes in the IT environment.
Implementation of Alerts
- Configuring Alerts: Configure monitoring tools to respond when thresholds are exceeded. Specify which metrics trigger an alert and define the severity levels (e.g., warning, critical).
- Integrate Communication Tools: Ensure alerts are integrated with communication tools like email, SMS, or incident management systems for timely notifications.
Best Practices for Alerts
- Prioritize and Categorize Alerts: Not all alerts are equally important. Prioritize them based on their impact on the business and categorize them so that responders can quickly understand their urgency.
- Avoid Over-Notification: Adjust the alert thresholds to report only meaningful deviations, reducing unnecessary noise.
- Regularly Review Alert Logic: Review the alert conditions and thresholds to refine them based on past incidents and evolving business needs.
Regular Audits and Fine-Tuning for Optimal Performance
Regular audits are essential to maintaining the optimal performance of middleware systems. Depending on the criticality of the applications supported, audits can be conducted quarterly or bi-annually. Methods should include automated monitoring tools and manual reviews to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Identifying Performance Gaps
Audits help identify performance gaps by comparing current performance data against established benchmarks. Analyzing trends over time can highlight recurring issues or degradation in performance, prompting further investigation.
Fine-Tuning Strategies
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: Adjust configurations to ensure resources are used efficiently.
- Updating Middleware: Leverage improvements from newer versions.
- Adjusting Load-Balancing: Ensure optimal performance by fine-tuning load-balancing configurations.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Middleware monitoring must comply with industry standards such as ISO/IEC 20000, ITIL, or specific compliance requirements like GDPR for data handling. These standards help ensure reliable, secure, and efficient operations.
Compliance Strategies
- Regular Training: Regular training sessions update teams on the latest standards.
- Conduct Compliance Audits: Regularly audit compliance with industry standards.
- Integrate Compliance Checks: Incorporate compliance checks into regular IT workflows.
- Automated Compliance Monitoring: Utilize tools to track and maintain compliance.
Documentation and Reporting
Thorough documentation and regular reporting are essential for compliance. Documentation should include configurations, changes made, and audit logs. Regular reports should be generated to demonstrate compliance to internal and external auditors.
Integration with Other IT Management Systems
Integrating middleware monitoring with other IT management systems, such as network management and application performance monitoring, can provide a holistic view of IT health. This integration helps quicker root cause analysis and enhances proactive IT infrastructure management.
Strategies for Effective Integration
- Standardized Interfaces: Use standardized interfaces and protocols for data exchange.
- Native Integration Capabilities: Choose tools that offer native integration capabilities.
- Central Repository: Maintain a central repository of monitoring data to enhance analysis and reporting.
Training and Capacity Building
IT staff must receive continuous training on new monitoring tools, best practices, and compliance requirements. Regular workshops and hands-on sessions can help build proficiency.
Developing Expertise
- Mentoring Programs: Implement mentoring programs to develop in-house expertise.
- Encourage Certifications: Encourage IT staff to obtain relevant certifications.
- Partnerships with Experts: Consider partnerships with external experts for specialized needs.
Now that we’ve explored the best practices for middleware monitoring, let’s look at the future trends shaping this field and how organizations can stay ahead in the evolving IT landscape.
Future Trends in Middleware Monitoring
As IT environments continue to evolve, middleware monitoring must adapt to meet new challenges and leverage emerging technologies. The future of middleware monitoring lies in automation, cloud-native solutions, proactive and predictive monitoring, and enhanced security measures. These trends promise to revolutionize how organizations manage their middleware ecosystems, ensuring greater efficiency, scalability, and resilience.
Current Challenges in Middleware Monitoring
Modern IT environments are becoming increasingly complex and dynamic, presenting several challenges for middleware monitoring:
- Complexity and Diversity: Organizations now operate with a mix of on-premises legacy systems and cloud-based services, creating a heterogeneous landscape that is difficult to monitor effectively.
- Dynamic Environments: The rise of microservices and containers has made IT environments more dynamic, requiring monitoring tools that can adapt quickly to changes.
- Data Overload: The vast amount of data generated by middleware components can overwhelm traditional monitoring tools, leading to inefficiencies and missed critical insights.
Automation in Middleware Monitoring
Automation is playing a pivotal role in modern middleware monitoring solutions. By streamlining processes and reducing manual workloads, automation enables IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives while ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and security.
Key Benefits of Automation
- Streamlined Issue Resolution: Automated workflows enable quick detection, diagnosis, and resolution of issues, minimizing downtime and maintaining service continuity.
- Proactive Performance Management: Automation allows for predictive analysis and the automatic adjustment of resources to prevent performance bottlenecks before they occur.
- Scalability and Adaptability: Automated monitoring scales seamlessly with growing IT infrastructures, ensuring consistent performance as environments expand.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Dynamically optimizes resource utilization based on workload demands, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced Compliance: Automatically enforces security policies, role-based access controls (RBAC), and audit trail logging to maintain regulatory compliance.
- Simplified Deployment and Configuration: Reduces manual setup efforts through automated discovery of middleware components and intelligent configuration adjustments.
- Data-Driven Insights: Leverages automation to analyze trends, generate reports, and deliver actionable insights for decision-making and continuous improvement.
By incorporating automation into middleware monitoring, organizations can reduce human error, improve response times, and ensure consistent adherence to best practices. Automation not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports the broader goals of scalability, security, and proactive management in dynamic IT landscapes.
The Impact of Cloud-Native Technologies on Middleware Monitoring
Cloud-native technologies such as Kubernetes and Docker have revolutionized middleware deployment. Monitoring solutions are evolving to address the specific needs of these environments:
Key Features of Cloud-Native Monitoring
- Container Monitoring: Tools that provide visibility into middleware running in containers.
- Service Mesh Observability: Gaining deep visibility into and control over the interactions between microservices to ensure performance and security.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-native monitoring solutions scale with the environment, ensuring consistent performance monitoring regardless of system size.
Cloud-Native Middleware Monitoring Solutions
Cloud-native middleware monitoring solutions are purpose-built to align with the principles and requirements of cloud-native architectures. Unlike traditional monitoring tools, which are often retrofitted for cloud environments, cloud-native monitoring solutions are designed to seamlessly integrate with containerized and orchestrated systems. They provide scalability, flexibility, and efficiency without introducing unnecessary complexity or overhead.
Advantages of Agentless Solutions
Agentless software is often considered more cloud-native due to its alignment with critical principles and advantages associated with cloud-native architectures:
- Scalability and Elasticity: Easily scales with the cloud environment.
- Resource Efficiency: Optimizes resource usage without the need for agents.
- Simplified Deployment: Reduces deployment complexity and maintenance efforts.
As middleware becomes increasingly integrated into cloud-native ecosystems, monitoring solutions must not only track performance but also proactively anticipate issues, optimize resource usage, and adapt to ever-changing environments. Cloud-native middleware monitoring is a vital enabler of operational efficiency, resilience, and innovation in the modern IT landscape.
Shift Towards Proactive and Predictive Monitoring
Proactive and predictive monitoring approaches are gaining traction over reactive methods. These approaches enable organizations to address potential issues before they impact users and align IT performance more closely with business objectives.
Key Benefits of Proactive and Predictive Monitoring
- Proactive Issue Resolution: Monitoring tools can now trigger automated workflows to address issues before they impact users.
- Enhanced Business Continuity Planning: Predictive insights help organizations prepare better for potential disruptions, ensuring smoother operations and minimizing downtime.
Evolving Security Measures in Monitoring Solutions
With the ever-growing threat landscape, future middleware monitoring solutions will prioritize advanced security measures. Incorporating advanced encryption, authentication protocols, and compliance features will safeguard sensitive data and ensure the integrity of monitoring processes.
Key Security Enhancements
- Advanced Encryption: Protects data during transmission and storage.
- Authentication Protocols: Incorporation of existing protocols ensures secure access without introducing new vulnerabilities. Automation of authentication updates to monitored elements ensures that only authorized users have access.
- Compliance Features: Incorporation of role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users can only see and act on what they’re authorized to, enhancing security and compliance.
Some solutions, like Infrared360, are already leading in this area, offering robust security features that align with these future trends.
Conclusion
Middleware monitoring is the cornerstone of maintaining a robust and efficient IT infrastructure in today’s complex digital landscape. Its ability to provide real-time visibility into system performance, optimize resource allocation, and preemptively address potential issues ensures seamless operations and reduces costly downtime. By investing in effective middleware monitoring solutions, businesses can enhance their IT performance, safeguard security and compliance, and achieve operational excellence. This critical capability supports scalability, adaptability, and business continuity, making it indispensable for modern organizations.
Organizations are encouraged to adopt advanced middleware monitoring tools, such as Infrared360’s monitoring solutions, to unlock the full potential of their IT environments. These tools not only streamline management processes but also provide actionable insights that empower IT teams to deliver consistent and exceptional performance across all middleware components.
For more information, check out the additional resources below or contact a middleware expert from Avada Software to discuss how to enhance and optimize your middleware environment.
Additional Resources
Recommended Reading and Whitepapers
- Monitoring Widely Distributed Environments Without Losing Focus
- Ensuring VNA’s Network Reliability with Avada Software’s Infrared360
- Alight Implements Secure, Holistic Self-Service Messaging
- Parker Hannifin Improves Efficiencies Across Business Units with Infrared360® and Trusted Spaces™
- SOMPO International Builds Business Platform Optimization with SOAP and REST Monitoring
- Tips for Administration and Troubleshooting of IBM MQ Across a Mixed OS Environment
- University of Oregon Middleware and Application Development
- Middleware Specialists LinkedIn Group
Links to In-Depth Guides
- Developing Governance and Naming Standards with IBM MQ
- What is Middleware?
- Middleware Concepts and Architecture
- Message Queueing Concepts
- Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) Explained
Relevant Webinars and Video Tutorials
- Managing Middleware in Hybrid Cloud
- The Business Case for Modernizing Your MQ Estate Today
- Improving Productivity Through Smart, Safe Self-Service
- Transforming Your IBM MQ Estate Using Containers
- Understanding External Influences on Your Integration Strategy and Direction
- What You Need To Know About Managing and Monitoring Kafka Transactions
- Ensuring Resilience: Mastering IBM MQ Failover, Backup, and High Availability
- Modernizing with Microservices and Containers
- IBM Message Queue Health Check & License Metric Requirements
- Middleware Explained